NAD+ and PEPTIDE THERAPY
Aging is an inevitable process of human life, a path we all travel naturally.
However, what is emerging in recent years is a new chapter in our understanding of aging and the possibilities of influencing it in a positive way.
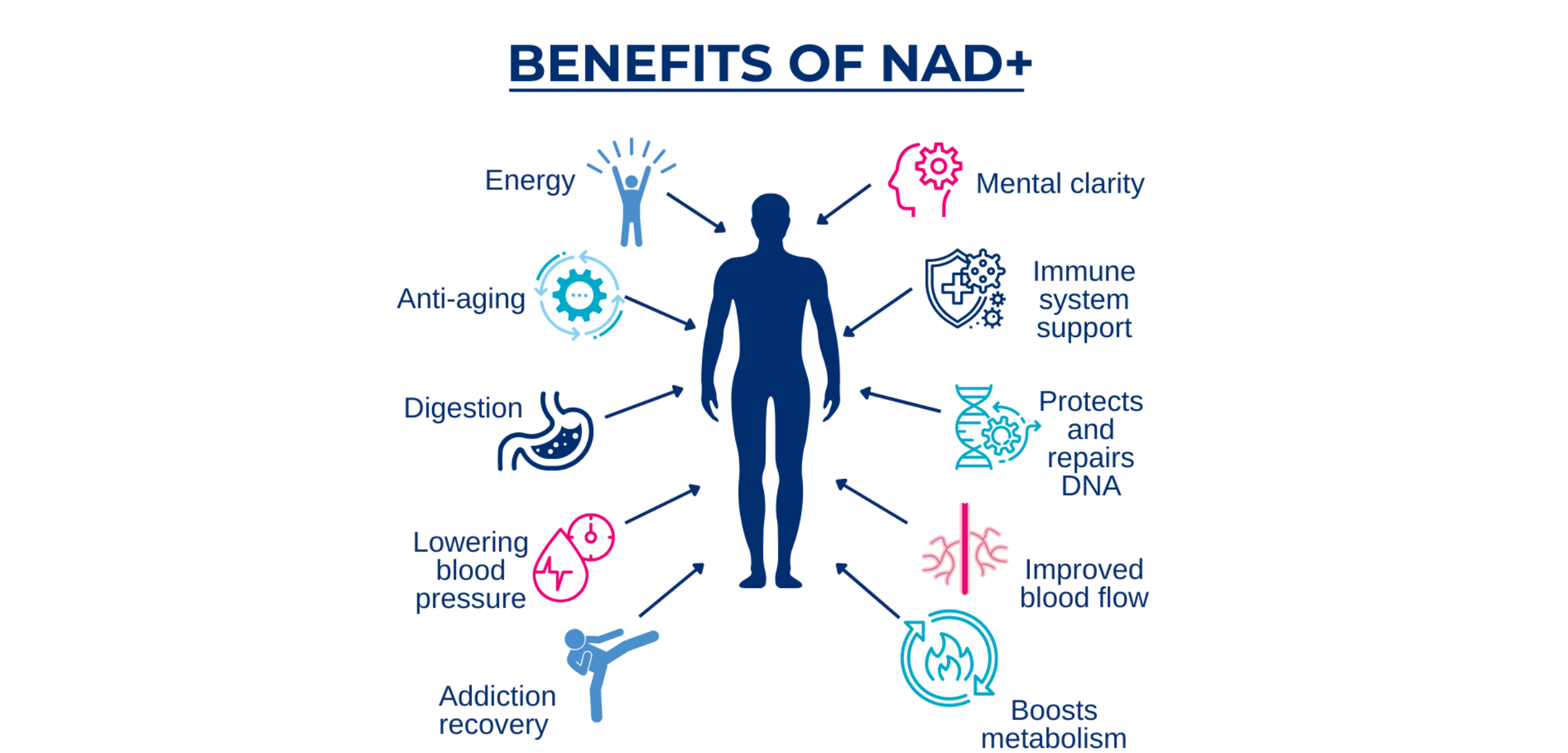
At the center of this scientific revolution is Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, known as NAD+, an extraordinary molecule that plays a crucial role in the functioning of our cells.
NAD+ is the vital energy that powers our existence, a kind of biological fuel that keeps our body’s engine running.
But NAD+ is much more than just an energy source.
It is a key player in the fight against aging and in promoting overall well-being.
In the United States, a fast-growing trend is gaining ground: “Peptide Therapy,” or peptide therapy.
This innovative medical approach is attracting attention because of its potential to improve health and fight aging in a targeted way.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of NAD+ and peptide therapy.
We will discover how these two powerful weapons come together to challenge the biological clock, offering a host of extraordinary benefits that go far beyond simply fighting aging.
It will be a journey of discovery into the future of anti-aging and total wellness, where science opens new doors to a healthy, vigorous, and vitality-filled life.
Get ready to unlock the secret of a life where time is no longer just an adversary, but an ally in our quest for optimal health.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a key molecule found in all cells of our body and is the oxidate of the coenzyme NADH.
The abbreviation stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, also commonly known as NAD+. (The “+” refers to the oxidized form of NAD).
Coenzymes such as NAD bind to our enzymes to help initiate and accelerate actions that are essential for the healthy function of our bodies.
NAD is a key component of body processes, such as:
REDOX REACTIONS:
- Energy Metabolism:
- NAD+ is like a key that starts the engine of cells to produce energy.
It works by taking in and giving away small particles called electrons during a process that takes place in the mitochondria, the “powerhouses” of our cells.
This passage of electrons helps create ATP, which is the “fuel” that cells use to make virtually everything.
- NAD+ is like a key that starts the engine of cells to produce energy.
- Oxidative Balance:
- NAD+ maintains the balance within our cells between two chemical states, one “oxidized” and one “reduced.”
This balance is critical because it protects cells from damage that can be caused when there are too many oxidative processes, (kind of like when rust attacks metal).
Maintaining this balance helps keep cells healthy and prevent damage that might otherwise make them age faster or function poorly.
- NAD+ maintains the balance within our cells between two chemical states, one “oxidized” and one “reduced.”
ENZYME ACTIVITIES:
- Metabolism Regulation:
Enzymes that require NAD+ to operate play a crucial role in converting the food we consume into energy ready to be used by our bodies.
During glycolysis, NAD+ turns into NADH, collecting electrons like a bus collecting passengers.This process takes place in the cytoplasm of cells and breaks down glucose, which we get from carbohydrates, into smaller molecules, releasing energy.
Next, in the Krebs cycle, which takes place in the mitochondria, NAD+ collects additional electrons and helps produce even more energy.
These steps are crucial because without them, cells could not sustain daily activities, such as movement, growth, and tissue repair.
- Circadian Rhythm:
NAD+ also plays an important role in regulating our internal biological clock, known as the circadian rhythm.
This rhythm determines when we feel tired and when we are awake and active.
Sirtuins, which are a type of protein that depend on NAD+, help regulate this cycle.
They function as conductors, making sure that the body’s various functions take place at the right time.
For example, sirtuins can influence when cells need to grow, repair themselves or produce energy. This is especially important at night, when the body is repairing and regenerating.
If NAD+ levels are low, the work of sirtuins can be impaired, leading to disturbed sleep and an irregular circadian rhythm, which can affect everything from our mood to our ability to concentrate and even metabolism.
CELLULAR FUNCTIONS:
- DNA repair:
DNA repair is a vital process that maintains the integrity of the genome and protects cells from damage that can lead to mutations and diseases, such as cancer.
NAD+ plays a central role in this process as the raw material for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARP), which are key enzymes in DNA repair.
When DNA suffers damage, such as that caused by UV radiation, toxic chemicals or oxidative stress, cells must act quickly to repair these lesions and prevent errors in DNA replication that could lead to mutations.
PARPs detect these breaks in DNA and use NAD+ to attach ADP-ribose groups to proteins, including themselves and other repair enzymes.
This process, known as poly(ADP-ribosylation), serves as a signal to recruit additional DNA repair factors to the site of damage and begins the repair process.
NAD+ is therefore essential for the function of PARPs.Without sufficient NAD+, PARPs cannot do their job effectively, which can lead to incomplete or incorrect DNA repair.
This can have long-term consequences for genome stability and may increase the risk of genetic disease development, accelerated aging, and carcinogenesis.In addition, poly(ADP-ribosylation) not only helps to repair DNA, but is also involved in the regulation of gene expression and programmed cell death (apoptosis), which are important processes in maintaining cellular homeostasis and cancer prevention.
- Cellular Senescence:
Cellular senescence is a biological phenomenon in which cells cease to divide and are in a state of growth arrest while remaining metabolically active.
This state is considered a protective response of the body against the potential development of cancerous cells.NAD+ is an important player in this process, as it supports the cellular functions that control senescence.When cells detect DNA damage, oncogenic activation (genes that, if mutated or inappropriately expressed, can cause cancer) or other types of cellular stress, they can enter a state of senescence.This mechanism is a kind of self-preservation program that prevents potentially harmful cells from multiplying.
NAD+ comes into play in several ways:
- Supporting DNA Repair:
As discussed above, NAD+ is essential for the functions of PARPs in DNA repair.
If DNA damage is too extensive and cannot be repaired, NAD+ helps facilitate the cell’s transition to senescence to prevent proliferation of cells with damaged DNA.
- Regulation of Gene Expression:
Through its role as a substrate for sirtuins, NAD+ influences the activity of these enzymes that can promote or suppress cellular senescence.
Sirtuins can deacetylate proteins that regulate the transcription of genes involved in senescence, thereby influencing cell fate.
- Modulation of Inflammation:
Cellular senescence is often associated with an inflammatory response.
NAD+ can modulate this response through sirtuins and other metabolic pathways, helping to control the inflammatory environment surrounding senescent cells.
- Cell Signaling:
Senescent cells release signaling factors that can induce senescence in other nearby cells or attract immune system cells to remove senescent cells.
NAD+ is involved in these signaling pathways, supporting cell communication and tissue homeostasis.
Cellular senescence is thus a defense mechanism against cancer, but excessive accumulation of senescent cells may contribute to aging and age-related diseases.
The management of NAD+ levels is therefore a delicate balance:
Enough NAD+ is needed to support cellular senescence and prevent cancer, but also to prevent the accumulation of senescent cells that can damage tissue and promote aging.
Research on NAD+ and cell senescence is particularly promising for the development of anti-aging and anti-cancer therapies, as it aims to optimize cell function and maintain the balance between preventing uncontrolled cell proliferation and maintaining healthy, functional tissue.
IMMUNE FUNCTION:
The immune system is the body’s defense against pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and other microorganisms that can cause disease.
NAD+ plays a crucial role in supporting this defense system in various ways, contributing to an effective and regulated immune response.
- Energy for Immune Cells:
Immune cells, like all other cells in the body, require energy to function properly.
NAD+ is critical for energy production in the mitochondria, providing the necessary fuel for immune cells to respond rapidly to pathogen invasion.
- Regulation of the Inflammatory Response:
NAD+ affects the function of sirtuins, which are involved in the regulation of inflammation.
A controlled inflammatory response is essential to fight infection without causing excessive damage to body tissues.
Uncontrolled chronic inflammation is a risk factor for many chronic diseases, including autoimmune disorders and cancer.
- Immune Cell Repair and Survival:
NAD+ helps in DNA repair and regulation of the life cycle of immune cells, including their growth, multiplication, and programmed death (apoptosis).
This ensures that immune cells are functional, ready to fight infection and can be renewed when needed.
- Cellular Signaling and Communication:
NAD+ is involved in the signaling pathways that allow immune cells to communicate with each other. This communication is vital to coordinate an immune response that is both rapid and accurate, ensuring that the body can specifically target pathogens without damaging healthy tissues.
- Antioxidant Response:
NAD+ also helps regulate oxidative stress in immune cells.
By maintaining a balance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants, NAD+ helps protect immune cells from internal damage that could impair their efficiency.
- Immune Metabolism Adaptation:
During an infection, immune cells can change their metabolism to adapt and respond more effectively.
NAD+ is involved in these metabolic changes, which may include an increase in glycolysis to produce energy more rapidly.
In summary, NAD+ is a multifunctional player in the immune system, contributing not only to the immediate response against infection but also to the maintenance of balanced and regulated immunity over the long term.
With age, NAD+ levels decline, which can adversely affect immune function. Therefore, maintaining adequate levels of NAD+ could be strategic for strengthening immunity, especially in the elderly or individuals with conditions that compromise the immune system.
The decline in NAD+ levels with advancing age is a phenomenon that has significant implications for health and well-being, affecting various aspects of biological function.
NEURONAL HEALTH:
Neurons are among the most metabolically active cells in the human body, with high energy requirements to support critical processes such as maintenance of membrane potential, electrical signal transmission, and neurotransmitter release.
These processes are critical for neural communication and the proper functioning of the nervous system as a whole.
NAD+ comes into play as a key molecule in the electron transport chain, a vital process that takes place in the mitochondria, where energy stored in nutrients is converted into ATP, the main energy currency of the cell.Without sufficient NAD+, the electron transport chain cannot function effectively, resulting in less optimal ATP production.
When neurons fail to produce enough ATP due to a deficiency of NAD+, several aspects of their function can be compromised:In conclusion, NAD+ is essential for neuronal health and function.
Its deficiency can have profound effects on brain health, potentially contributing to neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Therefore, maintaining adequate levels of NAD+ could be a therapeutic strategy to support brain function and combat age-related cognitive decline.
- Membrane Potential:
Neurons depend on ATP to maintain membrane potential, which is essential for the generation and conduction of nerve impulses.
Insufficient ATP production can reduce the ability of neurons to communicate effectively, affecting cognition and coordination.
- Membrane Potential:
- Synaptic Transmission:
The release of neurotransmitters at synapses is an energy-demanding process.
A deficit of NAD+ can lead to impaired or dysfunctional synaptic transmission, which can result in alterations in behavior, mood, and memory.
- Synaptic Transmission:
- Neuronal Repair and Maintenance:
Neurons use energy to repair DNA damage and to maintain the health of their structures, such as axons and dendrites.
NAD+ deficiency can therefore lead to inadequate maintenance of neurons, accelerating cognitive decline and increasing the risk of neurodegeneration.
- Neuronal Repair and Maintenance:
- Oxidative Stress:
NAD+ is also involved in the regulation of antioxidant responses.
Without sufficient NAD+ availability, neurons may become more susceptible to oxidative stress, which can damage cellular components and contribute to the death of the neurons themselves.
- Oxidative Stress:
BRAIN FUNCTION:
Optimal brain function depends on a complex network of neural communications, which in turn are regulated by a range of biochemical and cellular processes.
NAD+ plays an essential role in many of these processes, including the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are the molecules responsible for the transmission of signals between neurons.
- Synthesis of Neurotransmitters:
Neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, serotonin, and dopamine are synthesized through metabolic pathways that may require NAD+ as a cofactor.
These chemical molecules are essential for the regulation of mood, attention, arousal, and many other cognitive functions.
A deficiency in NAD+ can therefore lead to suboptimal production of neurotransmitters, resulting in a negative impact on synaptic communication and related brain functions.
- Modulation of Neuroprotective Processes:
NAD+ is involved in regulating the activity of sirtuins, a class of enzymes that promote cellular stress resistance and neuronal survival.
Sirtuins can influence the longevity of neural cells and protect them from damage, helping to prevent cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.Inadequate levels of NAD+ can limit the activity of these protective proteins, making neurons more vulnerable to various types of stress, including oxidative and inflammatory stress.
- Neuronal Plasticity:
Neuronal plasticity is the ability of neurons to change and adapt in response to experience, a fundamental process for learning and memory.
This includes the formation of new synaptic connections, the strengthening or weakening of existing synapses, and even neurogenesis, the creation of new neurons in the adult brain.
NAD+ supports neuronal plasticity not only by providing the energy needed for these processes, but also by participating in the regulation of gene expression and the modulation of synaptic activity.
A deficiency of NAD+ can therefore impair the brain’s ability to form new neural pathways and adapt to changes, negatively affecting learning and memory.
NAD+ is a crucial element in maintaining healthy brain function and promoting mechanisms that protect and enhance cognitive abilities.

CANCER PREVENTION:
- DNA repair:
DNA repair is essential to prevent mutations that can cause cancer. NAD+ is critical to this process because it helps enzymes repair and maintain DNA. Here are the simplified key points:
- PARP enzymes:
- They use NAD+ to signal and repair damaged DNA.
- If NAD+ is missing, DNA repair slows down, increasing the risk of cancerous mutations.
- Sirtuins:
- They depend on NAD+ to control DNA stability.
- Low levels of NAD+ reduce their activity, leaving DNA more exposed to damage that can lead to cancer.
In short, NAD+ is an ally in the fight against cancer because it supports our cells’ DNA repair systems.
Maintaining adequate levels of NAD+ could therefore help prevent the onset of cancer
Genetic Stability:NAD+ is also involved in maintaining chromosome stability and regulating gene expression. Insufficient levels of NAD+ can lead to genetic instability, another risk factor for cancer development.
SARCOPENIA:
- Energy Efficiency:
Muscle mass requires energy to maintain its function and structure.
As NAD+ decreases, mitochondria in muscles may become less efficient, reducing the ability of the muscle to work effectively and maintain its mass.
- Tissue Repair and Maintenance: NAD+ is necessary for tissue repair and regulation of inflammation.
A deficiency of it can impair the body’s ability to repair muscles after injury or after exercise, accelerating the loss of muscle mass and strength.
In summary, reduced NAD+ levels are a key factor in the acceleration of the aging process and the pathogenesis of age-related diseases.
Current research is focused on developing strategies to increase NAD+ levels, such as supplementation with NAD+ precursors (e.g., nicotinamide riboside or nicotinamide mononucleotide), to counteract these effects and promote health and longevity.
PETIDE THERAPY WITH NAD+
NAD+ Therapy and the Peptide Therapy Revolution: Discovering a Revolutionary Medical Approach
In the world of medicine and scientific research, there is a relentless search for innovative methods to improve health, delay aging, and promote overall well-being.
In this context, two major players are emerging as powerful allies in the fight against the signs of aging and health challenges: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, known as NAD+, and Peptide Therapy, or peptide therapy.
NAD+ has been shown to be a key molecule for cellular functioning, contributing to energy production, maintenance of DNA integrity, and metabolic efficiency.
Its importance in delaying aging and promoting longevity has become an increasingly promising field of research.
On the other hand, Peptide Therapy represents a revolutionary approach based on the use of peptides, short chains of amino acids, to specifically influence biological processes within the body.
These peptides are designed to target specific dysfunctions or imbalances, offering a targeted and personalized treatment option.
What makes this combination fascinating is how NAD+ therapy seamlessly integrates with Peptide Therapy, creating a powerful synergy in promoting wellness and combating aging.
IV Therapy with NAD+:
Intravenous Therapy (IV Therapy) with NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is described as one of the newest and most innovative options in the field of intravenous therapies.
NAD+ Treatment in Three Infusions: Maximizing the Benefits of IV Therapy:
The effectiveness of any treatment can often depend on how it is administered.
In the case of NAD+ therapy, one approach that is gaining popularity is that of three infusions spread over seven days.
This schedule is specifically designed to maximize the benefits of this revolutionary therapy.
As is well known, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) plays a crucial role in biological processes within cells, contributing to energy production, maintenance of DNA integrity, and a number of essential metabolic functions.
With the program of three infusions over seven days, an approach is taken that provides the body with measured and repeated doses of NAD+. Here’s how it works:
- Three Infusions of NAD+:
The treatment involves administering three infusions of NAD+ during the week.
These infusions can vary in dosage, usually between 300 mg or 750 mg, depending on the patient’s needs and medical indications.
- Distribution over Time:
Infusions are distributed over seven days, allowing the body to gradually and efficiently absorb additional NAD+.
This distribution strategy helps minimize side effects and maximize benefits.
- Multifactorial Benefits:
Therapy with three NAD+ infusions can offer several benefits.
In addition to improving energy levels and vitality, it can support DNA repair, metabolism, and even potential anti-aging effects.
The goal of this program is to provide targeted, individualized therapy tailored to each individual’s needs.
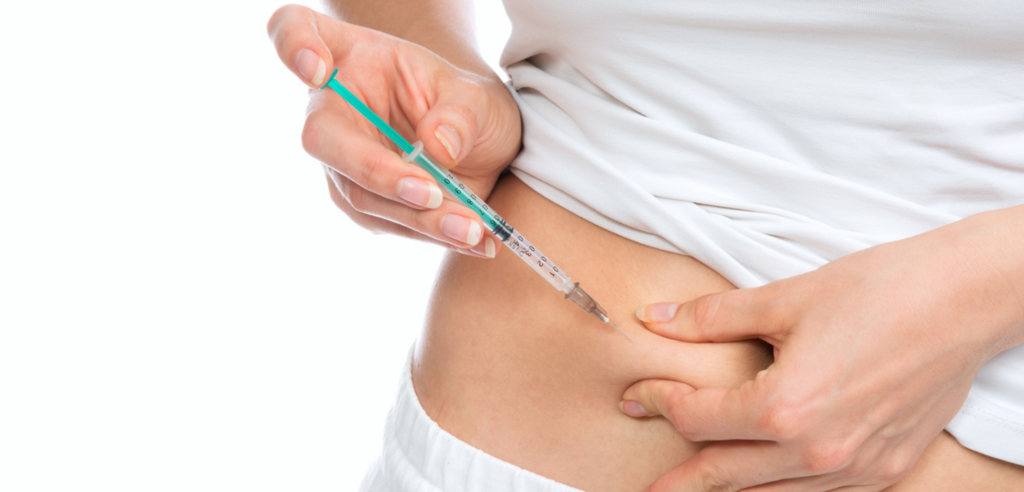
NAD+ PEPTIDE THERAPY with subcutaneous administration:
Innovative peptide therapy with NAD+ administered subcutaneously represents an emerging frontier in the landscape of anti-aging and biological function-enhancing treatments.
This mode of administration uses an extremely thin and short insulin needle that allows injection of the compound directly into the subcutaneous tissue, usually in the abdomen or upper thigh.
Advantages of Subcutaneous Administration over IV Therapy
One of the main advantages of this technique is the ability to self-manage the treatment.
Unlike intravenous (IV) therapy, which requires the presence and assistance of a nurse practitioner, subcutaneous administration can be performed by the patient himself after proper training.
This not only provides greater convenience and discretion but also reduces the cost of therapy.
In addition, while IV therapy can take several hours for slow drip administration of NAD+, subcutaneous therapy is completed in seconds without the need to be immobilized for the infusion time.
This aspect makes the treatment much more compatible with the dynamic and busy lifestyle of many patients.
Average Dosages and Treatment Protocol:
The average protocol dosage for peptide therapy with subcutaneous administration of NAD+ is 100 mg, administered twice a week.
This regimen maintains a steady release of NAD+ in the body, thereby supporting cellular functions and optimizing metabolic processes.
The treatment period can vary according to individual needs and therapeutic goals, extending from a minimum of one month to longer periods, always under the supervision of a physician.
Subcutaneous NAD+ peptide therapy is emerging as a valuable treatment option for those seeking a practical, less invasive approach to improving overall well-being and slowing the signs of aging.
As with any medical treatment, it is critical to consult a health care professional to customize the dosage and ensure that the treatment is appropriate and safe for the individual.