The drive for wellness,
health, and longevity is stronger than ever in today’s world, and within this movement, peptides have become a point of interest among athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and researchers. But what exactly are peptides?
How can they enhance our physical performance, health, and even extend longevity?
This article delves into these questions, offering a comprehensive look at the world of peptides.
What Are Peptides?
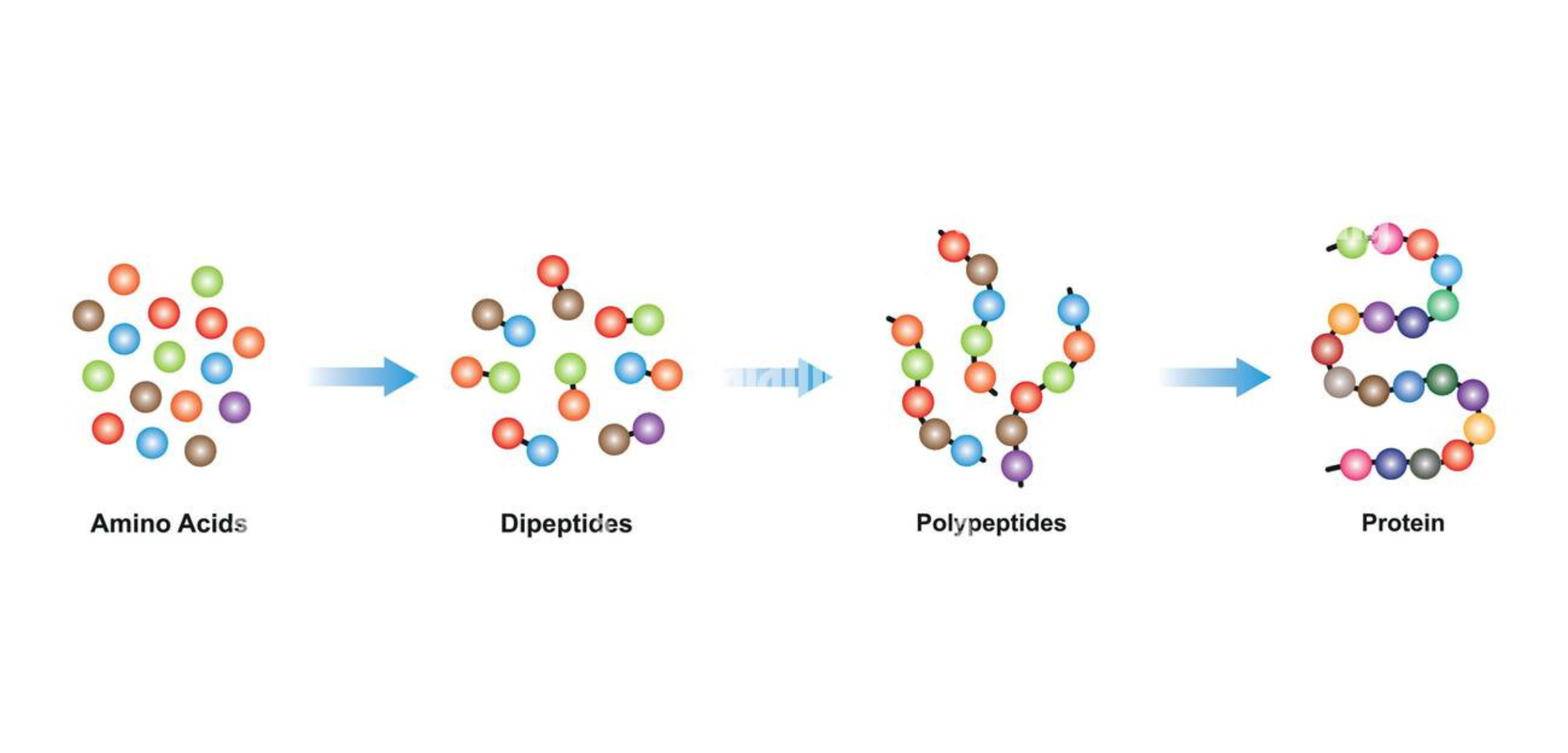
Peptides are molecules made of amino acids—the same fundamental units that make up proteins.
However, unlike proteins, peptides are composed of shorter amino acid chains.
These molecules are produced naturally by the body but can also be synthesized in laboratories.
Each peptide’s unique function depends on its specific amino acid composition and the sequence in which those amino acids are arranged.
More than 7,000 natural peptides have been identified, many of which play essential roles in human physiology.
Peptides can function as hormones, neurotransmitters, or growth factors, acting by interacting with specific receptors on cell surfaces, such as G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) or ion channels.
When these receptors are stimulated, they initiate a chain of reactions within cells.
Generally non-toxic to the body, peptides have long been used in treating hormone-dependent cancers, and in the 1980s, the development of sustained-release formulations like growth hormone and somatostatin expanded their clinical applications.
Therapeutic Peptides: A Key Class of Molecules
Therapeutic peptides, in particular, are short amino acid chains with significant potential for managing symptoms of various diseases and, in some cases, for treating these conditions directly.
In the pharmaceutical industry, peptides are typically defined as molecules with fewer than 100 amino acids, while longer chains form structures like monoclonal antibodies or proteins.
The Peptide Therapeutics Foundation defines a peptide as a molecule containing fewer than 50 amino acid residues, with a molecular weight below 5,000 Da.
In summary, therapeutic peptides represent a class of molecules with immense potential for treating a wide range of health conditions.
Key Benefits of Therapeutic Peptides
Therapeutic peptides offer several advantages that make them highly attractive for medical research and treatment:
•Specificity:
Peptides can be engineered to bind with high affinity to specific receptors, minimizing unwanted side effects.
•Effectiveness:
Peptides often prove more effective than small-molecule drugs, as they can target a broader range of receptors, including those typically inaccessible to small molecules.
•Safety:
Peptides are generally safer than small-molecule drugs, as they are made of amino acids—naturally occurring building blocks in the body.
•Versatility:
Peptides can be modified to improve their pharmacological properties, such as stability, effectiveness, and duration of action.
•Bioavailability:
Certain peptides can be administered non-invasively, like through inhalation or transdermal delivery, enhancing patient comfort and compliance.
•Low Toxicity:
Peptides generally exhibit low toxicity levels.
Despite these advantages, it’s important to note that using peptides as drugs presents some challenges, including their potential instability, the need for effective delivery systems, and the possibility of immune reactions.
How Peptides Work in the Body
Peptides play a variety of roles in the body, functioning as:
•Hormones:
Some peptides act as hormones—chemical messengers produced in one part of the body and transported through the bloodstream to exert effects elsewhere. For example, insulin is a peptide hormone that regulates blood glucose levels.
•Neurotransmitters:
Certain peptides function as neurotransmitters, chemicals that relay signals from one neuron to another. These peptides help regulate numerous bodily functions, including sleep, mood, pain response, and more.
•Growth Factors:
Some peptides, known as growth factors, are involved in regulating cell growth and division. For instance, epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulates cell growth and division in skin and other tissues.
In summary, peptides are essential to many biological processes in the body, serving as hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors.

A Brief History of Peptides
The discovery and development of peptides date back to the 19th century when biochemists began to uncover the composition of proteins.
As biotechnology advanced throughout the 20th century, interest in peptides surged, sparking exponential growth in research.
Peptides are defined as amino acid chains with a molecular weight under 5,000 daltons.
The simplest forms are dipeptides, composed of two amino acids connected by a single peptide bond, while longer chains are referred to as polypeptides.
Some well-known peptides include oxytocin, bradykinins, hypothalamic hormones, glutathione, and enkephalins.
Over time, scientists discovered that certain peptides could modulate physiological functions in humans and animals.
These have come to be known as bioactive peptides, with functions that include antihypertensive, immunomodulatory, antimicrobial, mineral-transport, and antiviral activities.
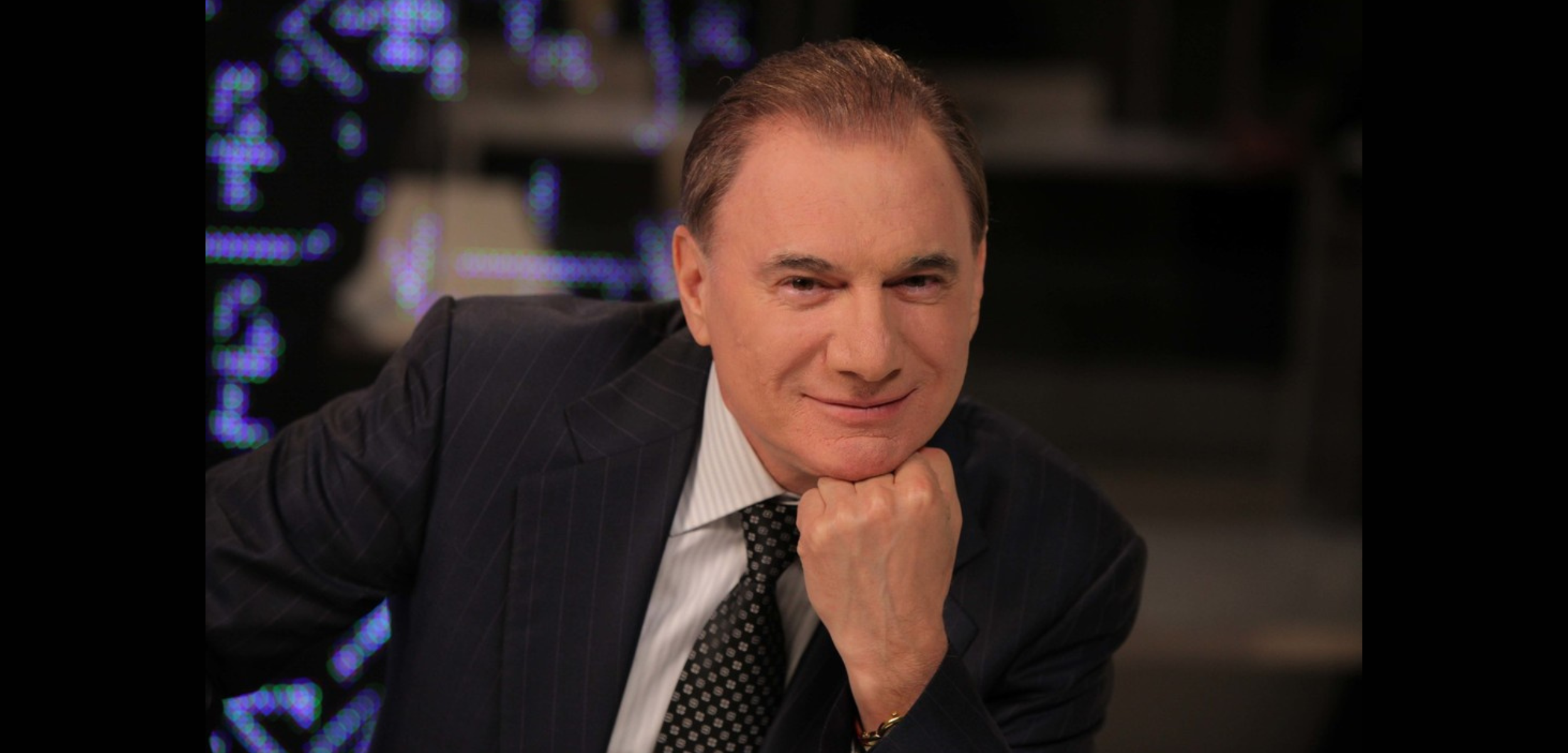
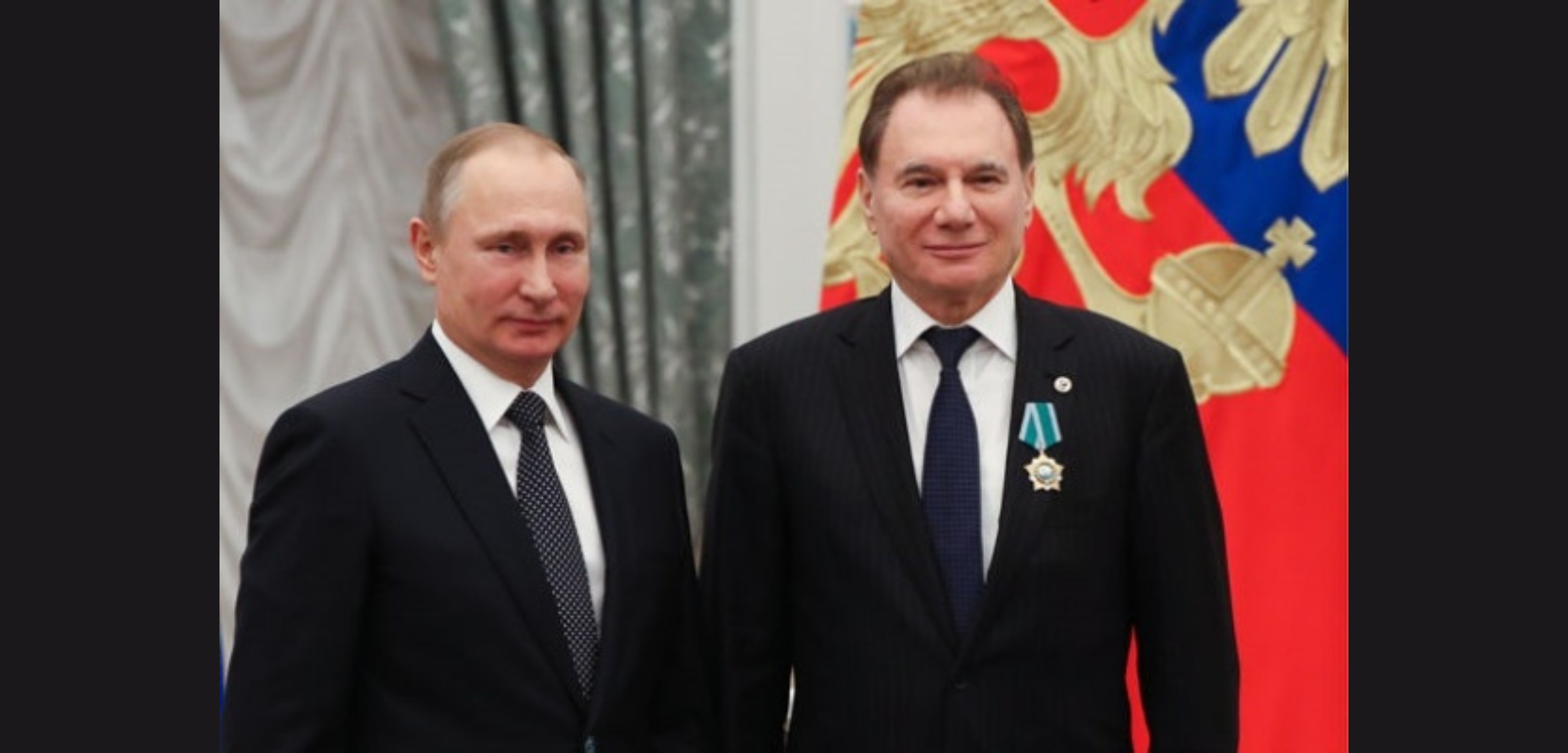
Professor Vladimir Khavinson and His Impact on Peptide Research
One of the pioneers in peptide research is Professor Vladimir Khavinson, a distinguished scientist known for his work on bioactive peptides and their potential in promoting health and combating aging.
Professor Khavinson has been instrumental in advancing the field of peptide-based therapies, particularly in anti-aging research.
Born on November 27, 1946, in Cottbus, Germany, Professor Khavinson is a prominent figure in gerontology.
He currently holds several prestigious positions, including Treasurer for the European region of the International Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics, Chief Gerontologist for the Health Committee of St. Petersburg, and Head of the Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology in St. Petersburg. He is also Vice President of the Gerontological Society of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Professor Khavinson is renowned for his groundbreaking research on bioregulatory peptides.
Over the last four decades, he has discovered, studied, and developed new classes of these peptides, particularly focusing on their role in regulating aging mechanisms.
His efforts have led to the development of peptide-based “geroprotectants”—drugs aimed at slowing down aging processes.
Through his research, Khavinson has introduced six peptide-based drugs and 64 peptide supplements into clinical practice.
His pioneering work helped establish gerontology and geriatrics as a scientific discipline within Russia’s national healthcare system. To date, he has mentored over 200 graduate and doctoral students from around the world.
Khavinson and his team have successfully isolated more than 20 active peptide complexes from various organs and synthesized an additional 15 peptides from amino acids.
This work resulted in the approval of six peptide-based medications for clinical use in the USSR, Russia, and later the CIS countries. Throughout his career, Khavinson has been granted 196 patents and authored 775 scientific publications.
His significant achievements are documented in his books Peptides and Aging and Gerontological Aspects of Genome Peptide Regulation.

Peptides and Athletic Performance
Peptides are widely recognized for their role in enhancing athletic performance.
Certain peptides, like CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin, are known for their ability to stimulate growth hormone production.
Growth hormone is essential for muscle development and maintenance, which in turn supports athletes in building strength and endurance.
Other peptides, such as BPC-157 and TB500, are valued for their healing properties, helping to accelerate recovery after injuries, reduce downtime, and enable athletes to quickly resume training.
Research on peptides extends beyond sports. These molecules are also gaining interest in the medical field, where studies are exploring their potential for treating various conditions, including cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Peptides and Fitness
Peptides can also play a key role in physical fitness and body composition. For example, peptides like AOD9604 and Fragment 176-191 are noted for their fat-reducing effects.
These peptides stimulate lipid metabolism and inhibit lipogenesis, the process by which glucose is converted to fat, resulting in reduced body fat and improved body composition for athletes.
Another peptide of interest is Melanotan II, which stimulates melanin production—the pigment that gives skin its tan.
Melanotan II enables athletes to achieve a long-lasting tan with less exposure to UV rays or tanning beds. Additionally, it can suppress appetite, further supporting weight management and body composition goals.
Peptides and Health
Peptides are remarkable molecules with a significant impact on human health.
For instance, PT-141 (Bremelanotide) is a peptide successfully used to treat sexual disorders by acting on the central nervous system to improve sexual function, offering a promising alternative to conventional treatments.
Another peptide, Semaglutide, has proven effective in managing type 2 diabetes.
Semaglutide mimics the action of incretin hormones, helping regulate blood sugar by stimulating insulin release and slowing digestion.
Thymosin Alpha-1 is yet another peptide with notable health benefits.
Known for its ability to modulate the immune system, it is used in treating certain infectious diseases and has shown promise in enhancing immune responses, making it a potential option for viral infections and certain types of cancer.
Peptides and Longevity
Peptides are emerging as an exciting area of research in the field of longevity.
Recent studies suggest that certain peptides, like Epitalon, may have anti-aging properties.
These effects are believed to stem from their ability to extend telomeres, the protective ends of chromosomes that tend to shorten with age—a process linked to aging and many age-related diseases.
Epitalon has shown potential in promoting telomere lengthening, supporting cellular health, and helping to delay aging.
Another peptide with anti-aging potential is 5-Amino 1MQ, which inhibits the enzyme NNMT (Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase), associated with fat accumulation and aging. By blocking NNMT, 5-Amino 1MQ may aid in weight management and help slow certain aging processes.

Peptides and the Future of Medicine
The interest in peptides as therapeutic tools continues to grow, with an increasing number of studies investigating their potential across various medical fields.
Peptides are now being explored for treating conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, infections, inflammation, and even neurodegenerative disorders.
For example, Semaglutide, used in treating type 2 diabetes, works by mimicking the action of the GLP-1 hormone (glucagon-like peptide-1), which stimulates insulin production during meals.
Semaglutide binds to and activates GLP-1 receptors, supporting improved blood sugar control.
Similarly, Thymosin Alpha-1 is used to enhance immune responses in cases of infectious diseases or immunodeficiency. By stimulating the maturation of T lymphocytes—critical cells in the immune system—Thymosin Alpha-1 has proven effective in treating some viral infections and bolstering immunity in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
5-Amino 1MQ, mentioned earlier, also holds promise in weight management and anti-aging, making it a noteworthy addition to the expanding field of peptide-based therapies.
The Role of Peptides in Biohacking
Biohacking involves using biological, chemical, nutritional, and physical interventions to optimize human well-being and performance.
Recently, peptides have gained popularity in biohacking for their abilities to enhance health, physical fitness, and cognitive function in various ways.
Some peptides are known for their anti-inflammatory effects, promoting cell regeneration, while others are valued for stimulating muscle growth or fat loss, making them popular among individuals seeking to improve their body composition and physical performance.
Additionally, certain peptides can enhance cognitive function.
Here are some peptides commonly used in biohacking:
•BPC-157:
Known for its wound-healing properties and effectiveness in improving intestinal health, BPC-157 can be administered subcutaneously but is generally ineffective when taken orally.
•TB-500:
Often used with BPC-157, TB-500 aids in wound healing and stimulates blood vessel formation.
•GHK-Cu:
This copper-based peptide supports tissue repair by promoting blood vessel and nerve growth and increasing collagen and elastin synthesis.
•Semax:
Known for its nootropic and neuroprotective effects, Semax is available as a nasal spray in some countries and can also be injected subcutaneously for quicker results.
•MK-677:
Although technically not a peptide, MK-677 mimics ghrelin, encouraging the release of growth hormone similarly to the effects of fasting.
•Epitalon:
Often regarded as the ultimate anti-aging peptide, Epitalon is studied for its potential to lengthen and protect telomeres, which naturally shorten with age.
Spotlight on Notable Peptides
The human body is a marvel of biological engineering, orchestrated by a network of molecules that sustain our health. Among these, peptides play a critical role. Below are some of the best-known peptides used in both therapeutic and research settings:
•CJC-1295:
A synthetic peptide renowned for stimulating growth hormone production, often combined with other growth hormone-releasing peptides like Ipamorelin to reduce body fat, increase muscle mass, and improve strength.
•HGH Fragment 176-191:
This fragment of human growth hormone is specifically designed to promote fat loss and is considered more effective in this regard than traditional HGH.
•Melanotan II:
Developed to stimulate melanin production, Melanotan II enables a lasting tan while helping reduce sunburn risk, making it valuable for skin cancer prevention.
•BPC-157: A peptide with powerful healing capabilities, BPC-157 is often used to accelerate the regeneration of damaged ligaments and tendons.
•TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4):
Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, TB-500 is used to promote tissue repair, particularly in musculoskeletal injuries.
•PT-141 (Bremelanotide):
Used to treat sexual disorders, PT-141 shows promise in addressing erectile dysfunction and hypoactive sexual desire disorder.
•AOD9604:
A growth hormone fragment designed for weight loss, AOD9604 promotes fat breakdown and inhibits fat formation, offering potential as an anti-obesity treatment.
•Ipamorelin:
This growth hormone-releasing peptide is valued for its ability to stimulate GH production with fewer side effects, such as water retention.
•Sermorelin:
Like CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin, Sermorelin stimulates natural GH production, often favored as a safer alternative to synthetic HGH.
•Thymosin Alpha-1:
Known to enhance immune function, this peptide is used in treating certain infections and strengthening the immune response, particularly in immunocompromised patients.
•Semaglutide:
A GLP-1 receptor agonist used to regulate blood sugar in type 2 diabetes and support weight loss by enhancing insulin release and inhibiting glucagon secretion.
•5-Amino 1MQ:
This peptide targets NNMT, an enzyme linked to fat accumulation and aging, potentially aiding in weight management and slowing age-related decline.
•Mod-GRF1:
Also known as CJC-1295 without DAC, this peptide encourages GH release without the side effects of excessive GH.
•Hexarelin:
One of the most potent peptides for promoting HGH production, Hexarelin supports muscle growth, tissue repair, and cardiac health.
•ACE-031:
Known for inhibiting myostatin, ACE-031 encourages muscle growth, making it of interest for muscle-wasting diseases.
•NAD+:
A coenzyme vital to cellular energy production, NAD+ levels are linked to improved cellular health and longevity.
•Semax:
Developed in Russia as a cognitive enhancer, Semax is known to improve memory and concentration and provide neuroprotective effects.
•Selank:
Another Russian-developed peptide, Selank has anxiolytic effects and is researched for its potential to treat anxiety and mood disorders.
•P21:
A nootropic peptide studied for its role in neurogenesis and potential to mitigate Alzheimer’s symptoms.
•PE-22-28:
Developed as a treatment for anxiety and depression, this peptide functions as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, boosting serotonin levels.
•DSIP (Delta Sleep Inducing Peptide):
Known for promoting restful sleep, DSIP is being studied for its potential in treating sleep disorders.
•Cerebrolysin:
This peptide improves memory and cognitive function, showing promise in treating dementia and neurodegenerative diseases.
•FOXO4-DRI:
This peptide targets senescent cells, potentially extending lifespan by supporting cellular health.
•Cartalax and Cortagen:
Both peptides aid in joint health by promoting cartilage regeneration and reducing inflammation.
•Cardiogen:
Focused on heart health, Cardiogen supports heart tissue regeneration and provides protective effects against ischemic conditions.
•PNC-27:
A cancer-targeting peptide currently under investigation for its ability to induce apoptosis in cancer cells.
•SS-31:
Known for supporting mitochondrial health, SS-31 reduces oxidative stress and promotes cellular energy production.
•B7-33:
A peptide with cardio-protective effects, B7-33 shows promise for treating heart failure by regenerating heart tissue.
•Humanin:
Known for its anti-aging properties, Humanin promotes mitochondrial health and provides neuroprotective benefits.
•Pinealon:
This brain-supporting peptide promotes neurogenesis and is being studied for its potential in treating neurodegenerative conditions.
•Testagen:
Developed to support muscle growth, Testagen promotes testosterone production and helps protect against muscle atrophy.
•VIP (Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide):
Known for modulating the immune system, VIP may protect against autoimmune diseases and support overall immune health.
The Future of Peptides in Health, Longevity, and Performance
Peptides represent a revolutionary frontier in medicine and biohacking, with vast potential to improve health, extend longevity, and enhance human performance.
Each peptide discussed here holds unique properties capable of influencing various aspects of bodily function, from growth hormone production and immune support to tissue repair and metabolic optimization.
They also offer potential solutions for a variety of disorders, including sexual health issues, and may help mitigate aging effects.
As with all biohacking and anti-aging therapies, the use of peptides should be based on scientific evidence and guided by qualified healthcare professionals.
While the future of peptides is promising, caution and responsibility are essential in their application.
We are only beginning to unlock the potential of these extraordinary molecules, and as science advances, peptides are likely to become key players in the quest to optimize human health and performance.







